Sum if equal to one of many things in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if equal to one of many things in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(SUMIF(range,things,values))
Explanation
If you need to sum values when cells are equal to one of many things, you can use a formula based on the SUMIF and SUMPRODUCT functions.
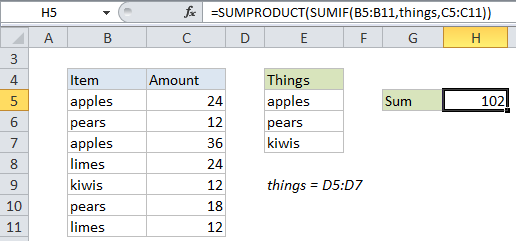
In the example shown, the formula in H5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(SUMIF(B5:B11,things,C5:C11))
How this formula works
The SUMIF function takes three arguments: range, criteria, and sum_range.
For range, we are using B5:B11. These cells contain the values we are testing against multiple criteria.
For criteria, we are using the named range “things” (E5:E7). This range contains the 3 values we are using as criteria. This range can be expanded to include additional criteria as needed.
For sum_range, we are using using C5:C11, which contains numeric values.
Because we are giving SUMIF more than one criteria, it will return multiple results – one result for each value in “things. The results come back an array like this:
=SUMPRODUCT({60;30;12})
SUMPRODUCT then sums all items in the array and returns a final result, 102.