Get last match cell contains in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Get last match cell contains in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=LOOKUP(2,1/SEARCH(things,A1),things)
Explanation
To check a cell for one of several things, and return the last match found in the list, you can use a formula based on the LOOKUP and SEARCH functions. In the case of multiple matches found, the formula will return the last match from the list of “things”.
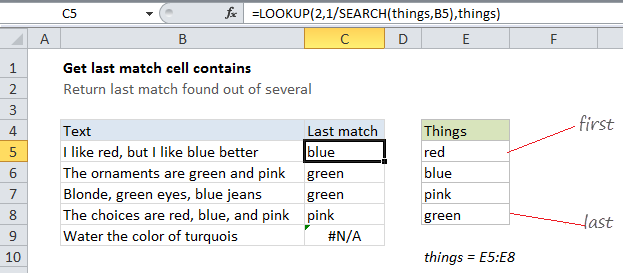
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=LOOKUP(2,1/SEARCH(things,B5),things)
How this formula works
Context: you have a list of things in the named range “things” (E5:E8), and you want to check cells in column B to see if they contain these things. If so, you want to return the last item from”things” that was found.
In this formula, the SEARCH function is used to search cells in column B like this:
SEARCH(things,B5)
When SEARCH finds a match, it returns the position of the match in the cell being searched. When search can’t find a match, it returns the #VALUE error. Because we are giving SEARH more than one thing to look for, it will return more than one result. In the example shown, SEARCH returns an array of results like this:
{8;24;#VALUE!;#VALUE!}
This array is then used as a divisor for the number 1. The result is an array composed of errors and decimal values. The errors represent things not found, and the decimal values represent things found. In the example shown, the array looks like this:
{0.125;0.0416666666666667;#VALUE!;#VALUE!}
This array serves as the “lookup_vector” for the LOOKUP function. The lookup value is supplied as the number 2, and the result vector is the named range “things”. This is the clever part.
The formula is constructed in such a way so that the lookup vector will never contain a value larger than 1, while the the lookup value is 2. This means the lookup value will never be found. In this case, LOOKUP will match the last numeric value found in the array, which corresponds to the last “thing” found by SEARCH.
Finally, using the named range “things” supplied as the result vector, LOOKUP returns the last thing found.
With hard-coded values
Using a range like “things” makes it easy to modify the list of search terms (and add more search terms), but it’s not a requirement. You can also hard-code values directly into the formula like this:
=LOOKUP(2,1/SEARCH({"red","blue","green"},B5),{"red","blue","green"})