Calculate running total in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Calculate running total in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUM($A$1:A1)
Explanation
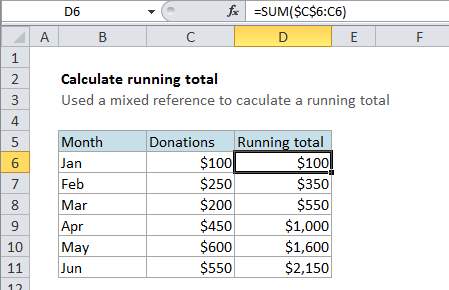
To calculate a running total, you can use the SUM formula with a mixed reference that creates an expanding range. In the example shown, the formula in cell D6 is:
=SUM($C$6:C6)
When this formula is copied down the column, it correctly reports a running total on each row.
How this formula works
This formula uses what is called a “mixed reference” to create an “expanding range”. A mixed reference is a reference that includes both absolute and relative parts.
In this case, the SUM formula refers to the range C6:C6. However, the first reference to C6 (on the left of the colon) is absolute and is entered $C$6. This “locks” the reference so that it won’t change when copied.
On the right of the colon, the reference is relative, and appears as C6. This reference will change as the the formula is copied down the column.
The result is a range that expands by one row each time it is copied down:
=SUM($C$6:C6) // formula in D6 =SUM($C$6:C7) // formula in D7 =SUM($C$6:C8) // formula in D8