Convert Text to Numbers in Excel
By default, text is left-aligned and numbers are right-aligned in Excel.
Atimes user enter inverted comma before inputting data values in a cell which automatically converts a number to text.
This example teaches you how to convert ‘text strings that represent numbers’ to numbers.
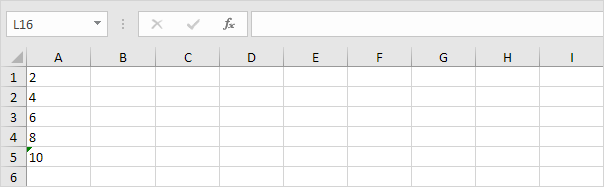
1. Select the range A1:A4 and change the number format to General.
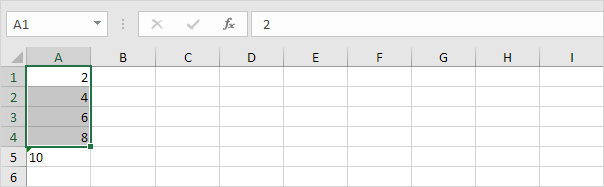
2. Numbers preceded by an apostrophe are also treated as text. Select cell A5 and manually remove the apostrophe.
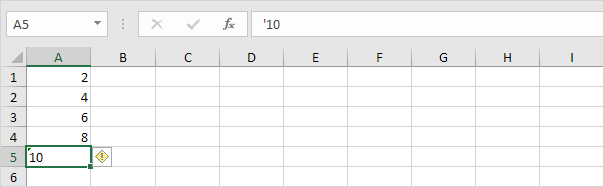
3a. You can also combine step 1 and 2 by adding an empty cell to the range A1:A5. By doing this, you let Excelknow that these text strings are numbers. Copy an empty cell.
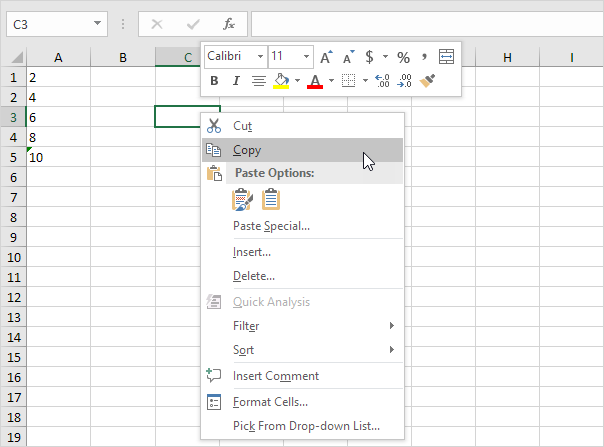
3b. Select the range A1:A5, right click, and then click Paste Special.
3c. Click Add.
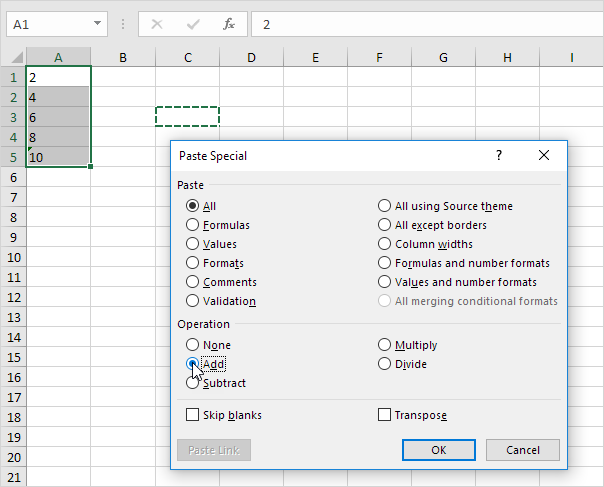
3d. Click OK.
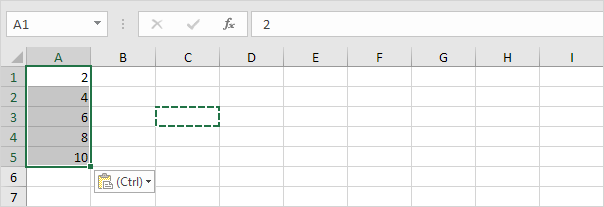
Result. All numbers are right-aligned and treated as numbers.
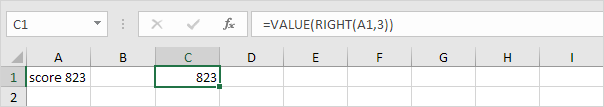
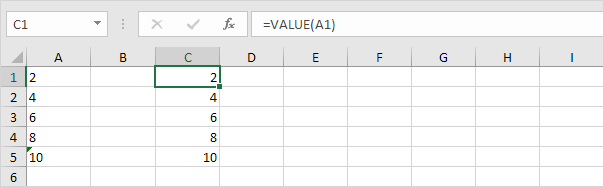
4a. You can also use the VALUE function.
4b. Here’s another example. Use the Right function (or any other text function) to extract characters from a text string and then use the VALUE function to convert these characters to a number.