Count total matches in two ranges in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count total matches in two ranges in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(range1,range2))
Explanation
If you want to compare two ranges, and count total matches between the two ranges, you can use a formula that combines the COUNTIF and SUMPRODUCT functions.
Context
Suppose you have a “master” list of some kind, and also have another list that contains some of the same items. You want a formula that compares the values in the 2nd list to see how many of them appear in the first list. You don’t care about the order that the items — you just want to know how many items in list 2 appear in list 1.
Solution
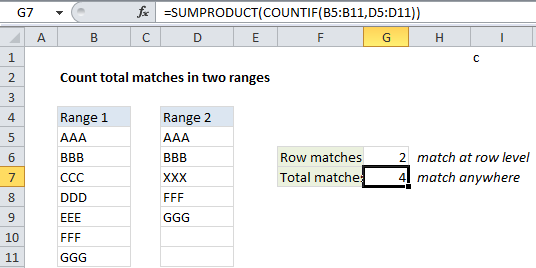
The formula we are using in cell G7 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(B5:B11,D5:D11))
Note that this formula does not care about the location or order of the items in each range.
Explanation
The COUNTIF function will count things in a range that meet your criteria. Normally, you would give COUNT if a range like A1:A10 and a simple criteria like “>10”. COUNTIF would then return the count of cells in A1:A10 that are greater than 10.
In this case however, we are giving COUNTIF a range for criteria. We aren’t using any logical operators, which means COUNTIF will check for equivalency (i.e. it behaves as if we used the equals (=) operator).
Because we give COUNTIF a range (also called an “array”) that contains 7 items, COUNTIF will return an array of 7 items as a result. Each item in the result array represents a count. In the example, this array that COUNTIF returns looks like this:
{1;1;0;1;1;0;0}
Now we simply need to add up the items in this array, which is a perfect job for SUMPRODUCT. The SUMPRODUCT function is a versatile function that handles arrays natively without any special array syntax.
If you give SUMPRODUCT two or more arrays, it will multiple the arrays together, sum up the results, and return that number. In this case, we give SUMPRODUCT just one array, so it simply sums up the items in the array and returns 4 as the result.
Match across rows
If you want to compare two ranges or columns, and want to count matches at the row level (i.e. only count matches when the same item appears in the same position), you’ll need a different formula.