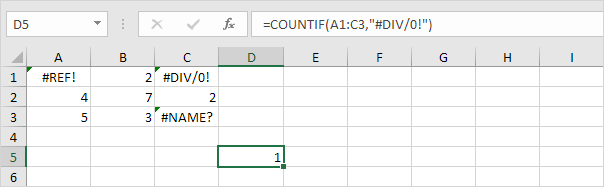
Count Errors in Excel
IF function and ISERROR function are used to check for an error in Excel.
This example shows you how to create an array formula that counts the number of errors in a range.
1. We use the IF function and the ISERROR function to check for an error in the record below:
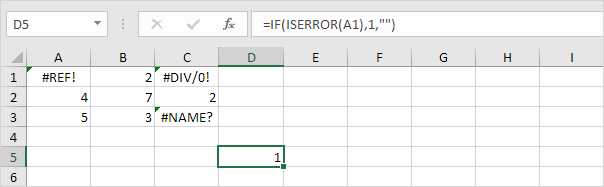
Explanation: the IF function returns 1, if an error is found. If not, it returns an empty string.
2. To count the errors (don’t be overwhelmed), we add the COUNT function and replace A1 with A1:C3.
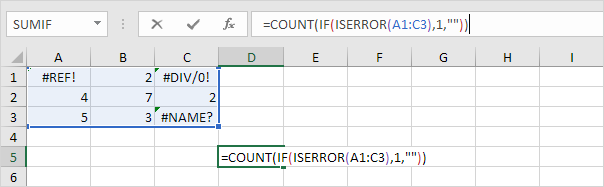
3. Finish by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER.
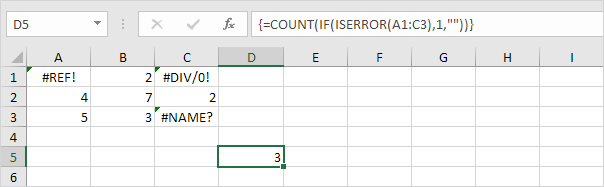
Note: The formula bar indicates that this is an array formula by enclosing it in curly braces {}. Do not type these yourself. They will disappear when you edit the formula.
Explanation: The range (array constant) created by the IF function is stored in Excel’s memory, not in a range. The array constant looks as follows:
{1,””,1;””,””,””;””,””,1}
This array constant is used as an argument for the COUNT function, giving a result of 3.
4. To count specific errors, use the COUNTIF function. For example, count the number of cells that contain the #DIV/0! error.