Get days between dates in Excel
To calculate the number of days between two dates you can simply subtract the older date from the newer date. The result will be an integer that represent the days between dates.
Formula
=later_date-earlier_date
Explanation
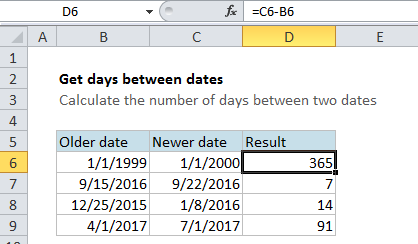
In the example shown, the formula in D6 is:
=C6-D6
The result is 365, since there are 365 days between 1/1/1999 and 1/1/2000.
Note: make sure you format the result with the General number format.
How this formula works
Dates in Excel are simply serial numbers that start on 1/1/1900.
In the example, the formula in cell D6 simply subtracts the numeric value of 1/1/1999 (36161) from the numeric value of 1/1/2000 (36526) to get a result of 365. The steps look like this:
=C6-B6 =1/1/1999-1/1/2000 =36161-36526 =365
Working with today
If you need to calculate the number of days between an earlier date and today, use:
=TODAY()-earlier_date
To calculate the number of days between a later date and today, use:
=later_date-TODAY()
Note that TODAY will recalculate on an on-going basis. If you open the workbook at a later date, the value used for TODAY will update and you will get a new result.