Display the current date and time in Excel
This tutorial show how to Display the current date and time in Excel using the example below.
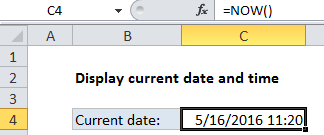
If you need to display the current date and time in a worksheet, you can use the NOW function. The date and time will update whenever the worksheet is recalculated or opened.
Formula
=NOW()
Explanation of how this formula works
The NOW function takes no arguments; it is entered with empty parentheses. When you enter the NOW function in a cell, it will display the current date and time. Each time the worksheet is recalculated or opened, the date and time will be updated. To display only the time component, format the cell using a time format. If you want to display the only the date, you can format the cell with a date format that does not display time, or you can use the TODAY function, which only inserts the date component.
Fixed time
If you need to insert the current date and time in a way that will not change, use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + ‘
This shortcut will insert the current time in a cell as a value that will not automatically change. If you need to insert both the date and time in a cell, use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + ; Then enter a space character and press Ctrl + Shift + ;