Excel Advanced Lookup using Index and Match Functions
Instead of using VLOOKUP, Use INDEX and MATCH and become an Excel pro. . To perform advanced lookups, you’ll need INDEX and MATCH.
Match
The MATCH function returns the position of a value in a given range. For example, the MATCH function below looks up the value 53 in the range B3:B9.
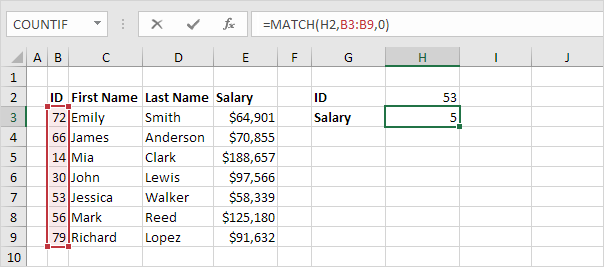
Explanation: 53 (first argument) found at position 5 in the range B3:B9 (second argument). In this example, we use the MATCH function to return an exact match so we set the third argument to 0.
Index
The INDEX function below returns a specific value in a one-dimensional range.
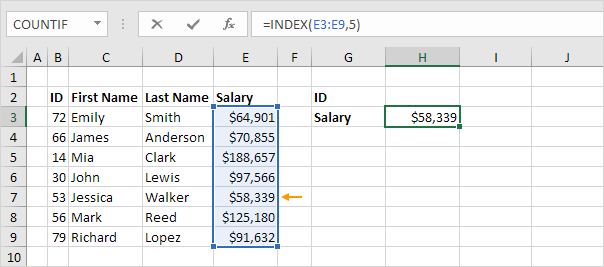
Explanation: the INDEX function returns the 5th value (second argument) in the range E3:E9 (first argument).
Index and Match
Replace the value 5 in the INDEX function (see previous example) with the MATCH function (see first example) to lookup the salary of ID 53.
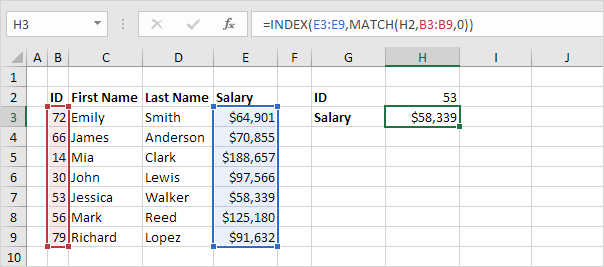
Explanation: the MATCH function returns position 5. The INDEX function needs position 5. It’s a perfect combination. If you like, you can also use the VLOOKUP function. It’s up to you. However, you’ll need INDEX and MATCH to perform advanced lookups, as we will see next.
Two-way Lookup
The INDEX function can also return a specific value in a two-dimensional range. For example, use the INDEX and the MATCH function in Excel to perform a two-way-lookup.

Case-sensitive Lookup
By default, the VLOOKUP function performs a case-insensitive lookup. However, you can use the INDEX, MATCH and the EXACT function in Excel to perform a case-sensitive lookup.
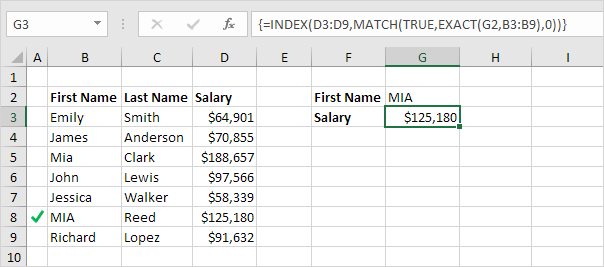
Note: the formula correctly looks up the salary of MIA Reed, not Mia Clark.
Left Lookup
The VLOOKUP function only looks to the right. No worries, you can use the INDEX and the MATCH function in Excel to perform a left lookup.

Note: when we drag this formula down, the absolute references ($E$4:$E$7 and $G$4:$G$7) stay the same, while the relative reference (A2) changes to A3, A4, A5, etc.
Two-column Lookup
Do you want to look up a value based on multiple criteria? Use the INDEX and the MATCH function in Excel to perform a two-column lookup.
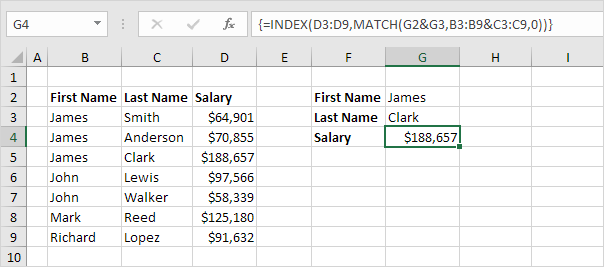
Note: the array formula above looks up the salary of James Clark, not James Smith, not James Anderson.
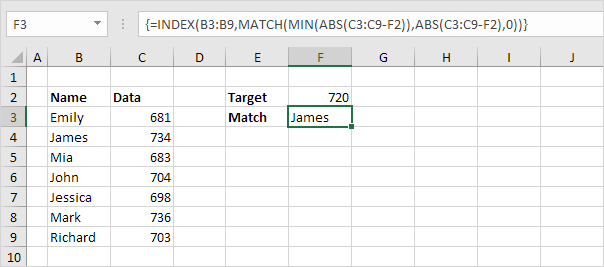
Closest Match
To find the closest match to a target value in a data column, use the INDEX, MATCH, ABS and the MIN function in Excel.