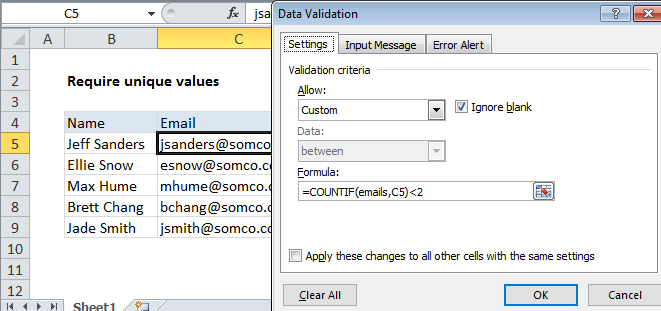
Excel Data validation unique values only
Reject duplicate data entry in a cell range.
To allow only unique values in a given range, you can use data validation with a custom formula based on the COUNTIF function.
Formula
=COUNTIF(range,A1)<2
Note: Cell references in data validation formulas are relative to the upper left cell in the range selected when the validation rule is defined, in this case B5.
Explanation
In the example shown, the data validation applied to C5:C9 is:
=COUNTIF(emails,C5)<2
where emails is the named range C5:C9.
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value. In this example, we are using a formula that checks that the input doesn’t already exist in the named range “emails”:
COUNTIF(ids,B5)<2
COUNTIF returns a count of the value in C5 inside the named range emails (C5:C9). If the count is less than 2, the expression returns TRUE and validation succeeds. If not, the expression returns FALSE and validation fails.