Sum Largest Numbers using LARGE function in Excel
LARGE function example shows you how to create an array formula that sums the largest numbers in a range.
Syntax:
LARGE(array, k)
Returns the k-th largest value in a data set. You can use LARGE to return the highest, runner-up, or third-place score.
For example,
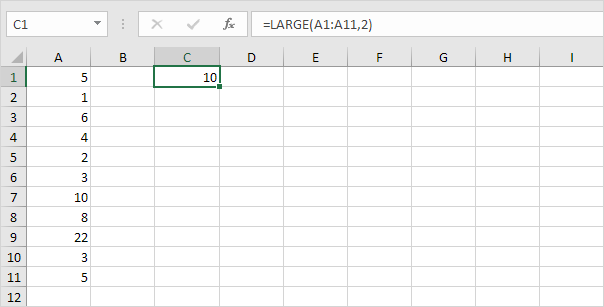
1. Find the second to largest number, use the following function.
2. To sum the 4 largest numbers (don’t be overwhelmed), add the SUM function and replace 2 with {1,2,3,4}.
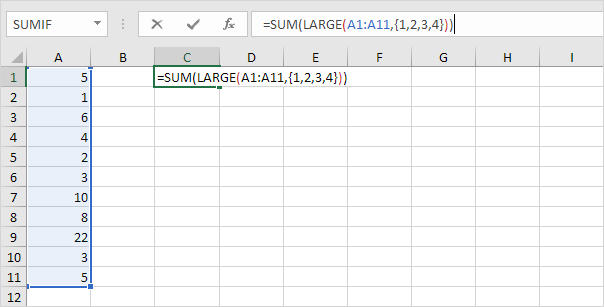
3. Finish by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER.
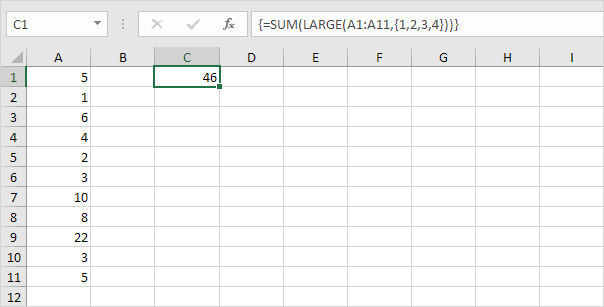
Note: The formula bar indicates that this is an array formula by enclosing it in curly braces {}. Do not type these yourself. They will disappear when you edit the formula.
Explanation: The range (array constant) created by the LARGE function is stored in Excel’s memory, not in a range. The array constant looks as follows.
{22,10,8,6}
This array constant is used as an argument for the SUM function, giving a result of 46.