How to convert numbers to text using TEXT function in Excel
To convert numbers into text values, you can use the TEXT function.
Normally, you want to maintain numeric values in Excel, because they can be used in formulas with other numbers. However, there are situations where converting numbers to text makes sense. For example, you might want to perform a lookup on numbers using wildcards, which can’t be done with numeric values.
Formula
=TEXT(A1,"0")
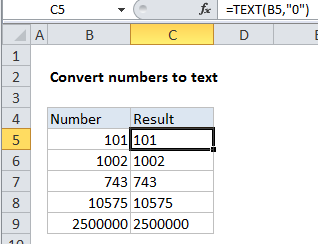
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=TEXT(B5,"0")
How this formula works
The TEXT function accepts a number as the first argument, something called “format_text” as the second. The format_text argument works like a number format, and specifies the formatting that should be used when converting the number to text. You can apply all the standard number formats that Excel provides, including dates, times, currency, and so on.
In the example, we are converting the number to text with no special formatting, so we simply use “0”. The result is the number as a text string. Visit Convert Numbers to Text to see other examples.