CONFIDENCE.NORM function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is CONFIDENCE.NORM function in Excel?
Syntax of CONFIDENCE.NORM function
CONFIDENCE.NORM(alpha,standard_dev,size)
The CONFIDENCE.NORM function syntax has the following arguments:
- Alpha Required. The significance level used to compute the confidence level. The confidence level equals 100*(1 – alpha)%, or in other words, an alpha of 0.05 indicates a 95 percent confidence level.
- Standard_dev Required. The population standard deviation for the data range and is assumed to be known.
- Size Required. The sample size.
CONFIDENCE.NORM formula explanation
- If any argument is nonnumeric, CONFIDENCE.NORM returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If alpha ≤ 0 or alpha ≥ 1, CONFIDENCE.NORM returns the #NUM! error value.
- If standard_dev ≤ 0, CONFIDENCE.NORM returns the #NUM! error value.
- If size is not an integer, it is truncated.
- If size < 1, CONFIDENCE.NORM returns the #NUM! error value.
- If we assume alpha equals 0.05, we need to calculate the area under the standard normal curve that equals (1 – alpha), or 95 percent. This value is ± 1.96. The confidence interval is therefore:
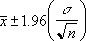
Example of CONFIDENCE.NORM function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Data | Description | |
| 0.05 | Significance level | |
| 2.5 | Standard deviation of the population | |
| 50 | Sample size | |
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =CONFIDENCE.NORM(A2,A3,A4) | Confidence interval for a population mean. In other words, the confidence interval for the underlying population mean for travel to work equals 30 ± 0.692952 minutes, or 29.3 to 30.7 minutes. | 0.692952 |