SUM function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is SUM function in Excel?
SUM function is one of Math and Trig functions in Microsoft Office Excel that adds all numbers in a range of cells and returns the result.
Syntax of SUM function
The syntax for the SUM function in Microsoft Excel is:
SUM( number1, [number2, ... number_n] )
OR
SUM ( cell1:cell2, [cell3:cell4], ... )
Note: You can sum combinations of both numbers and ranges of cells using the SUM function.
SUM formula explanation
- number
- A numeric value that you wish to sum.
- cell
- The range of cells that you wish to sum.
Returns
The SUM function returns a numeric value.
Example
Let’s look at some Excel SUM function examples and explore how to use the SUM function as a worksheet function in Microsoft Excel:
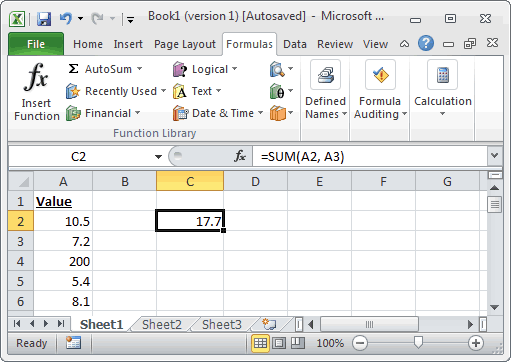
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following SUM examples would return:
=SUM(A2, A3) Result: 17.7 =SUM(A3, A5, 45) Result: 57.6 =SUM(A2:A6) Result: 231.2 =SUM(A2:A3, A5:A6) Result: 31.2 =SUM(A2:A3, A5:A6, 500) Result: 531.2