Display Date is workday in Excel
This tutorial show how to Display Date is workday in Excel using the example below.
To determine if a date is a workday or not, you can use a formula based on the WORKDAY function.
=WORKDAY(date-1,1,holidays)=date
Explanation of how this formula works
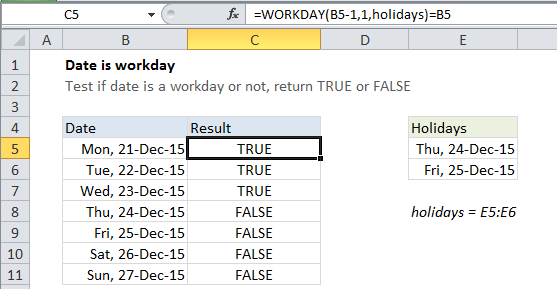
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=WORKDAY(B5-1,1,holidays)=B5
which returns TRUE, since Monday, Dec. 21, 2015 is a workday.
The WORKDAY function calculates dates in the future or past that are (by definition) “workdays”. In other words, WORKDAY automatically excludes weekends and (optionally) holidays.
WORKDAY accepts 3 arguments: start_date, days, and an (optionally) holidays.
In this case, we supply (date – 1) for start_date, 1 for days, and the named range “holidays” (E5:E6) for holidays.
This causes WORKDAY to step back one day, then add 1 day to the result, taking into account weekends and holidays. Effectively, we are “tricking” WORKDAY into evaluating the start_date. (Unfortunately, the cleaner syntax WORKDAY(date,0) doesn’t work).
When the date falls on a weekend or holiday, WEEKDAY will automatically adjust the date forward to the next working day.
Finally, we compare the original start_date to the the result of the WORKDAY function. If the dates are the same (i.e. the result of WORKDAY equals the start_date, the formula returns TRUE. If not, the formula returns FALSE.
Ensure a calculated date falls on a workday
To make sure any calculated date lands on a business day, just use the following formula:
=WORKDAY(calc_date-1,1,holidays)