Extract word that begins with specific character in Excel
To extract words that begin with a specific character, you can use a formula based on six functions: TRIM, LEFT, SUBSTITUTE, MID, LEN, and REPT. This approach is useful if you need to extract things like a Twitter user name from a cell that contains other text.
Formula
=TRIM(LEFT(SUBSTITUTE(MID(text,FIND("@",
txt),LEN(text))," ",REPT(" ",100)),100))
Note: 100 represents the longest word you expect to find that begins with the special character. Increase or decrease to suit your needs.
Explanation
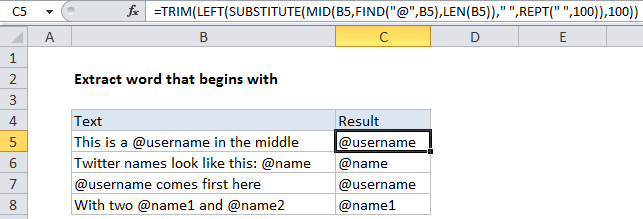
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=TRIM(LEFT(SUBSTITUTE(MID(B5,FIND("@",
B5),LEN(B5))," ",REPT(" ",100)),100))
How this formula works
Starting from the inside out, the MID function is used to extract all text after “@”:
MID(B5,FIND("@",B5),LEN(B5))
The FIND function provides the starting point, and for total characters to extract, we just use LEN on the original text. This is a bit sloppy, but it avoids having to calculate the exact number of characters to extract. MID doesn’t care if this number is bigger than the remaining characters, it simply extracts all text following “@”.
Next, we “flood” the remaining text with space characters, by replacing any single space with 100 spaces using a combination of SUBSTITUTE and REPT:
SUBSTITUTE("@word and remaining
text"," ",REPT(" ",100))
This seems crazy, but the logic becomes clear below.
Next, to extract just the word we want (i.e. @word), we use LEFT to extract the first 100 characters from the left. This gets us “@word”, plus many extra spaces. To visualize, the hyphens below represent spaces:
@word———————
Now we just need to remove all extra spaces. For that, we use the TRIM function.