Sum if cell contains text in another cell in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if cell contains text in another cell in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMIF(range,"*"&A1&"*",sum_range)
Explanation
To sum if cells contain specific text in another cell, you can use the SUMIF function with a wildcard and concatenation. In the example shown, cell G6 contains this formula:
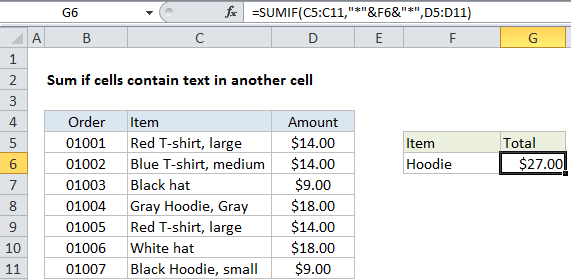
=SUMIF(C5:C11,"*"&F6&"*",D5:D11)
This formula sums amounts for items in column C that contain “hoodie”, anywhere in the cell.
How the formula works
The SUMIF function supports wildcards. An asterisk (*) means “zero or more characters”, while a question mark (?) means “any one character”.
Wildcards allow you to create criteria such as “begins with”, “ends with”, “contains 3 characters” and so on.
So, for example, you can use “*hat*” to match the text “hat” anywhere in a cell, or “a*” to match values beginning with the letter “a”.
In this case, we want to match the text in F6. We can’t write the criteria like “*F6*” because that will match only the literal text “F6”.
Instead, we need to use the concatenation operator (&) to join a reference to F6 to asterisks (*):
"*"&F6&"*"
When Excel evaluates this argument inside the SUMIF function, it will “see” “*hoodie*” as the criteria:
=SUMIF(C5:C11,"*hoodie*",D5:D11)
SUMIF then returns the sum for items that contain “hoodie”, which is $27.00 in the example shown.
Note that SUMIF is not case-sensitive.
Alternative with SUMIFS
You can also use the SUMIFS function. SUMIFS can handle multiple criteria, and the order of the arguments is different from SUMIF. The equivalent SUMIFS formula is:
=SUMIFS(D5:D11,C5:C11,"*"&F6&"*")
Notice the sum range always comes first in the SUMIFS function.