Dynamic Named Range in Excel
A dynamic named range expands automatically when you add a value to the range.
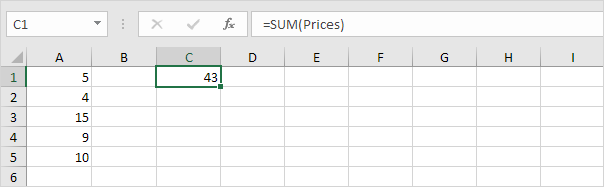
1. For example, select the range A1:A4 and name it Prices.
2. Calculate the sum.
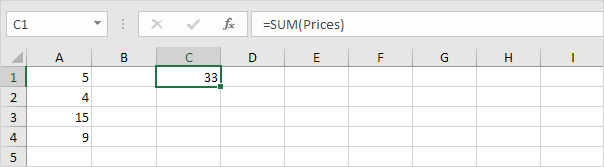
3. When you add a value to the range, Excel does not update the sum.
To expand the named range automatically when you add a value to the range, execute the following the following steps.
4. On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click Name Manager.
5. Click Edit.
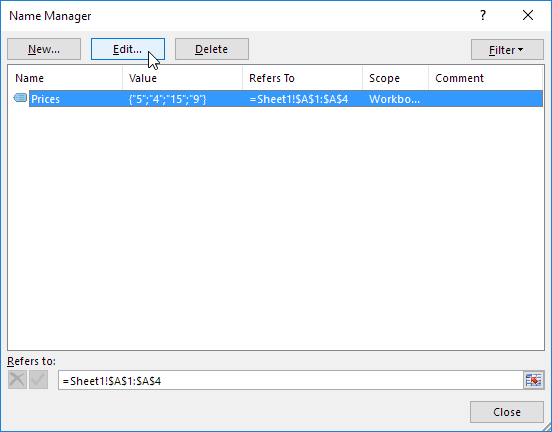
6. Click in the “Refers to” box and enter the formula =OFFSET($A$1,0,0,COUNTA($A:$A),1)
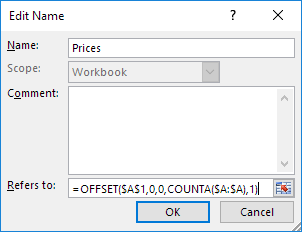
Explanation: the OFFSET function takes 5 arguments. Reference: $A$1, rows to offset: 0, columns to offset: 0, height: COUNTA($A:$A), width: 1. COUNTA($A:$A) counts the number of values in column A that are not empty. When you add a value to the range, COUNTA($A:$A) increases. As a result, the range returned by the OFFSET function expands.
7. Click OK and Close.
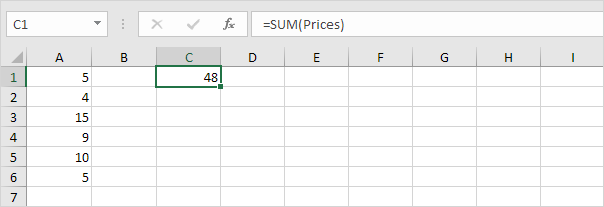
8. Now, when you add a value to the range, Excel updates the sum automatically.