Count paired items in listed combinations in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count paired items in listed combinations in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=COUNTIFS(range,”*”&$item1&”*”,range,”*”&item2&”*”)
Explanation
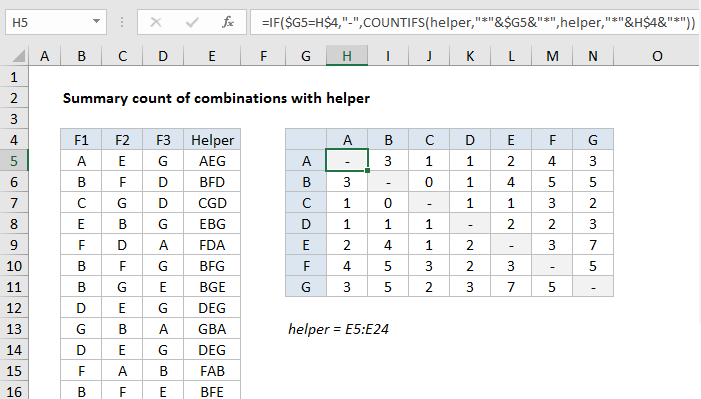
To build a summary table with a count of paired items that appear in a list of existing combinations, you can use a helper column and a formula based on the COUNTIFS function. In the example shown the formula in cell H5 is:
=IF($G5=H$4,"-",COUNTIFS(helper,"*"&$G5&"*",helper,"*"&H$4&"*"))
where helper is the named range E5:E24.
Note: this formula assumes items don’t repeat in a given combination (i.e. AAB, EFE are not valid combinations).
How this formula works
We want to count how often items in columns B, C, and D appear together. For example, how often A appears with C, B appears with F, G appears with D, and so on. This would seem like a perfect use of COUNTIFS, but if we try to add criteria looking for 2 items across 3 columns, it isn’t going to work.
A simple workaround is to join all items together in a single cell, then use COUNTIFS with a wildcard to count items. We do that with a helper column (E) that joins items in columns B, C, and D using the CONCAT function like this:
=CONCAT(B5:D5)
In older versions of Excel, you can use a formula like this:
=B5&C5&D5
Because repeated items are not allowed in a combination, the first part of the formula excludes matching items. If the two items are the same, the formula returns a hyphen or dash as text:
=IF($G5=H$4,"-"
If items are different, a COUNTIFS function is run:
COUNTIFS(helper,"*"&$G5&"*",helper,"*"&H$4&"*")
COUNTIFS is configured to count “pairs” of items. Only when the item in column G and the corresponding item from row 4 appear together in a cell is the pair counted. A wildcard (*) is concatenated to both sides of the item to ensure a match will be counted no matter where it appears in the cell.