Group numbers at uneven intervals in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Group numbers at uneven intervals in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=LOOKUP(value,intervals,groups)
Explanation
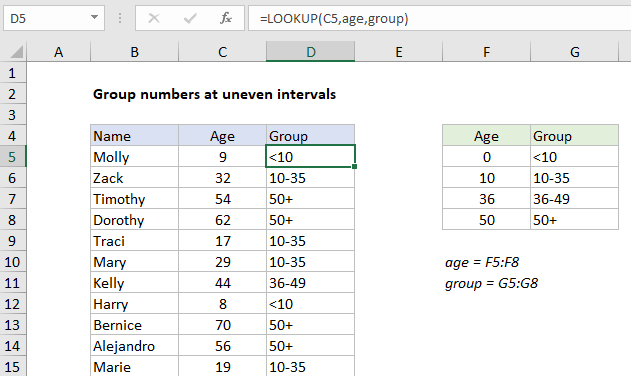
To group numbers into intervals of unequal size, you can use the LOOKUP function. In the example shown, the LOOKUP function is used to group people by age into at intervals of unequal size. The formula in D5 is:
=LOOKUP(C5,age,group)
Where “age” is the named range F5:F8 and “group” is the named range G5:G8.
How this formula works
To do this, LOOKUP is configured as follows:
- Lookup values are ages in column C
- The lookup vector is the named range “age” (F5:F8)
- The result vector is the named range “group” (G5:G8)
With this setup, LOOKUP performs an approximate match on the numeric values in column F, and returns the associated value from column G.
The LOOKUP function always performs an approximate match, with the following behavior:
- If LOOKUP finds an exact match in the age column, the corresponding group is returned.
- If no exact match is found, LOOKUP will traverse the age column until a larger value is found, then “step back” to the previous row.
- If an age is greater than 50 (the highest value), LOOKUP will return the group associated with 50 (“50+”).
- If age is less than the smallest value in the age column, LOOKUP will return #N/A.
Note: ages must appear in ascending order. Double-check custom intervals – it’s easy to make a mistake 🙂
With hardcoded values
If you want to do this kind of grouping without a table on the worksheet, you can hardcode values into LOOKUP as array constants like this:
=LOOKUP(C5,{0,10,36,50},{"<10","10-35","36-49","50+"})