Highlight column differences in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Highlight column differences in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=$A1<>$B1
Explanation
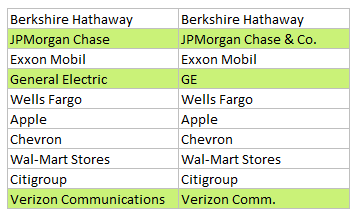
If you want to highlight the differences between two columns of data with conditional formatting you can do so with a simple formula that uses the” not equal to” operator (e.g. <>) and mixed references.
For example, if you have similar data in B2:B11 and C2:C11, and you want to highlight cells where values differ, select the data in both columns, starting from B2, and use this formula:
=$B2<>$C2
Note: with conditional formatting, it’s important that the formula be entered relative to the “active cell” in the selection, which is assumed to be B2 in this case.
How this formula works
When you use a formula to apply conditional formatting, the formula is evaluated relative to the active cell in the selection at the time the rule is created. In this case, the rule is evaluated for each of the 20 cells in the two columns of data.
The references to $B2 and $C2 are “mixed” – the column is locked, but the row is relative – so only the row number will change as the formula is evaluated. Whenever two values in a row are not equal, the formula returns TRUE and the conditional formatting is applied.
A case-sensitive option
By the “equals to” and “not equals to” operators (= and <>) are not case-sensitive. If you need a case-sensitive comparison, you can use the EXACT function with NOT, like so:
=NOT(EXACT($B2,$C2))
Exact performs a case-sensitive comparison and returns TRUE when values match. NOT reverses this logic so that the formula returns TRUE only when the values don’t match.