How to get top level domain (TLD) in Excel
To extract the top level domain (called “TLD”) from a list of domain names or email addresses, you can use a rather complex formula that uses several functions. In the formula below, domain represents a domain or email address in normal “dot” syntax.
Formula
=RIGHT(domain,LEN(domain)-FIND("*",SUBSTITUTE(domain,".","*",
LEN(domain)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(domain,".","")))))
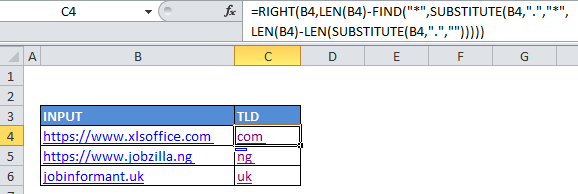
Explanation
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=RIGHT(B4,LEN(B4)-FIND("*",SUBSTITUTE(B4,".","*",LEN(B4)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B4,".","")))))
How the formula works:
At the core, this formula uses the RIGHT function to extract characters starting from the right.
The other functions in this formula just do one thing: they figure out how many characters need to be extracted.
At a high level, the formula replaces the last dot “.” in the domain with an asterisk “*” and then uses FIND to locate the position of the asterisk. Once the position is known, the RIGHT function can extract the TLD.
You may wonder how the formula knows to replace only the last dot?
This is the clever part of the formula.
The key is this part:
SUBSTITUTE(B4,".","*",LEN(B4)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B4,".","")))
which does the actual replacement of the last dot with “*”.
The trick is that SUBSTITUTE has a forth (optional) argument that specifies which “instance” of the find text should be replaced. If nothing is supplied for this argument, all instances are replaced. However, if, say the number 2 is supplied, only the second instance is replaced.
So, the formula needs to figure out which instance to replace, which is done here:
LEN(B4)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B4,".",""))
The length of the domain without any dots is subtracted from the full length of the domain. The result is the number of dots in the domain.
In the example name in B4, there are two dots in the domain, so the number 2 is used as in the instance number:
SUBSTITUTE(B4," ","*",2)
This replaces only second dot with “*”. The name then looks like this:
“www.domain*com”
The FIND function then takes over to figure out exactly where the asterisk is in the text:
FIND("*", "www.domain*com")
The result is 11 (the * is in the 11th position) which is subtracted from the total length of the domain:
LEN(B4)-11
Since the name is 15 characters, we have:
14-11 = 3
Finally, the number 3 is used by RIGHT like so:
=RIGHT(B4,3)
Which results in “com”
So there you have it. That’s how this formula extracts only the top level domain from a full domain name or email address.