Return blank if in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate Return blank if in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(A1=1,B1,"")
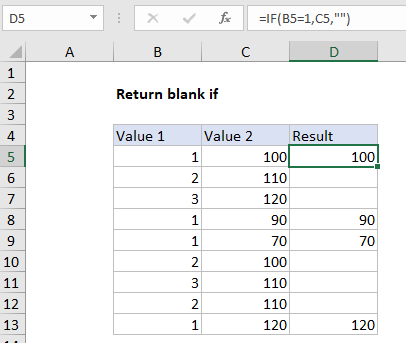
Explanation
To return a blank result using the IF function, you can use an empty string (“”). In the example shown, the formula in D5 (copied down) is:
=IF(B5=1,C5,"")
How this formula works
This formula is based on the IF function, configured with a simple logical test, a value to return when the test is TRUE, and a value to return when the test is FALSE. In plain English: if Value 1 equals 1, return Value 2. If Value 1 is not 1, return an empty string (“”).
Note if you type “” directly into a cell in Excel, you’ll see the double quote characters. However, when you enter as a formula like this:
=""
You won’t see anything, the cell will look blank.
Also, if you are new to Excel, note numeric values are not entered in quotes. In other words:
=IF(A1=1,B1,"") // right =IF(A1="1",B1,"") // wrong
Wrapping a number in quotes (“1”) causes Excel to interpret the value as text, which will cause logical tests to fail.
Checking for blank cells
If you need check the result of a formula like this, be aware that the ISBLANK function will return FALSE when checking a formula that returns “” as a final result. There are other options however. If A1 contains “” returned by a formula, then:
=ISBLANK(A1) // returns FALSE =COUNTBLANK(A1) // returns 1 =COUNTBLANK(A1)>0 // returns TRUE