IF function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is IF function in Excel?
IF function is one of logical functions in Microsoft Office Excel that returns one value if the condition is TRUE, or another value if the condition is FALSE.
Syntax of IF function
The syntax for the IF function in Microsoft Excel is:
IF( condition, value_if_true, [value_if_false] )
IF formula explanation
- condition
- The value that you want to test.
- value_if_true
- It is the value that is returned if condition evaluates to TRUE.
- value_if_false
- Optional. It is the value that is returned if condition evaluates to FALSE.
Returns
The IF function returns value_if_true when the condition is TRUE.
The IF function returns value_if_false when the condition is FALSE.
The IF function returns FALSE if the value_if_false parameter is omitted and the condition is FALSE.
Example of IF function
Let’s explore how to use the IF function as a worksheet function in Microsoft Excel.
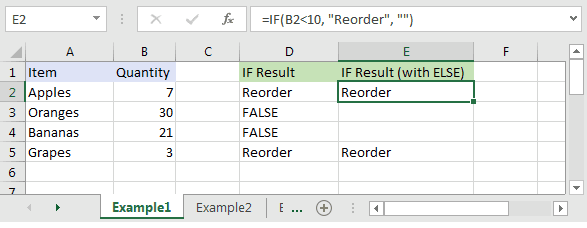
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following IF examples would return:
=IF(B2<10, "Reorder", "") Result: "Reorder" =IF(A2="Apples", "Equal", "Not Equal") Result: "Equal" =IF(B3>=20, 12, 0) Result: 12