IFS function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is IFS function in Excel?
IFS function is one of the Logical functions in Microsoft Excel that checks whether one or more conditions are met, and returns a value that corresponds to the first TRUE condition. IFS can take the place of multiple nested IF statements, and is much easier to read with multiple conditions.
Syntax of IFS function
Generally, the syntax for the IFS function is:
=IFS([Something is True1, Value if True1,Something is True2,Value if True2,Something is True3,Value if True3)
Examples of IFS function
Example 1
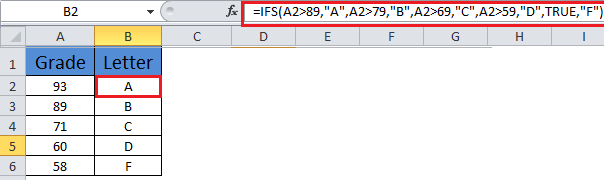
- =IFS(A2>89,”A”,A2>79,”B”,A2>69,”C”,A2>59,”D”,TRUE,”F”)
Which says IF(A2 is Greater Than 89, then return a “A”, IF A2 is Greater Than 79, then return a “B”, and so on and for all other values less than 59, return an “F”).
Example 2
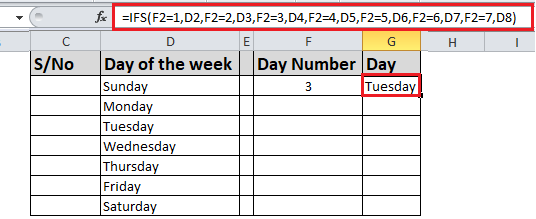
The formula in cell G7 is:
- =IFS(F2=1,D2,F2=2,D3,F2=3,D4,F2=4,D5,F2=5,D6,F2=6,D7,F2=7,D8)
Which says IF(the value in cell F2 equals 1, then return the value in cell D2, IF the value in cell F2 equals 2, then return the value in cell D3, and so on, finally ending with the value in cell D8 if none of the other conditions are met).
IFS formula explanation
- To specify a default result, enter TRUE for your final logical_test argument. If none of the other conditions are met, the corresponding value will be returned. In Example 1, rows 6 and 7 (with the 58 grade) demonstrate this.
- If a logical_test argument is supplied without a corresponding value_if_true, this function shows a “You’ve entered too few arguments for this function” error message.
- If a logical_test argument is evaluated and resolves to a value other than TRUE or FALSE, this function returns a #VALUE! error.
- If no TRUE conditions are found, this function returns #N/A error.
Important! Please note that the IFS function allows you to test up to 127 different conditions. However, we don’t recommend nesting too many conditions with IF or IFS statements. This is because multiple conditions need to be entered in the correct order, and can be very difficult to build, test and update.