Basic error trapping example in Excel
To catch errors that a formula might trigger in a worksheet, you can use the IFERROR function to display a custom message, or nothing at all. See example below:
Formula
=IFERROR(formula,value_if_error)
Explanation
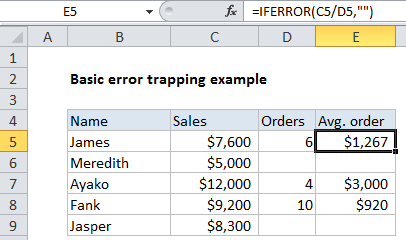
In the example shown, the formula in E5 is:
=IFERROR(C5/D5,"")
How this formula works
In this example, the IFERROR function is used to trap and suppress the #DIV/0! error that occurs when there is no value for Orders (column D). Without IFERROR, the formula C5/D5 would display a #DIV/0! error in E6 and E9.
The IFERROR function takes two arguments: a value (usually entered as a formula), and a result to display if the formula returns an error. The second argument is only used if the first argument throws an error.
In this case, the first argument is the simple formula for calculating the average order size, which divides total sales by the order count:
=C5/D5
The second argument is entered as an empty string (“”).
When the formula returns a normal result, the result is displayed.
When the formula returns #DIV/0!, an empty string is returned and nothing is displayed.